Chapter Table of Contents
Ch. 6 ConditionalsSection Table of Contents
Logical operators are binary operators that allow you to combine different boolean expressions (a boolean expression is basically something that can evaluate to either
true or false). Look at the tables below to learn about them. The tables are divided into 2 sections: a truth table, and examples. For the truth table section, p refers to any boolean expression.For a deeper explanation, you can also watch this Crash Course video (note: don’t worry too much about the logic gates and transistors — focus on what AND, OR, XOR, and NOT mean conceptually).
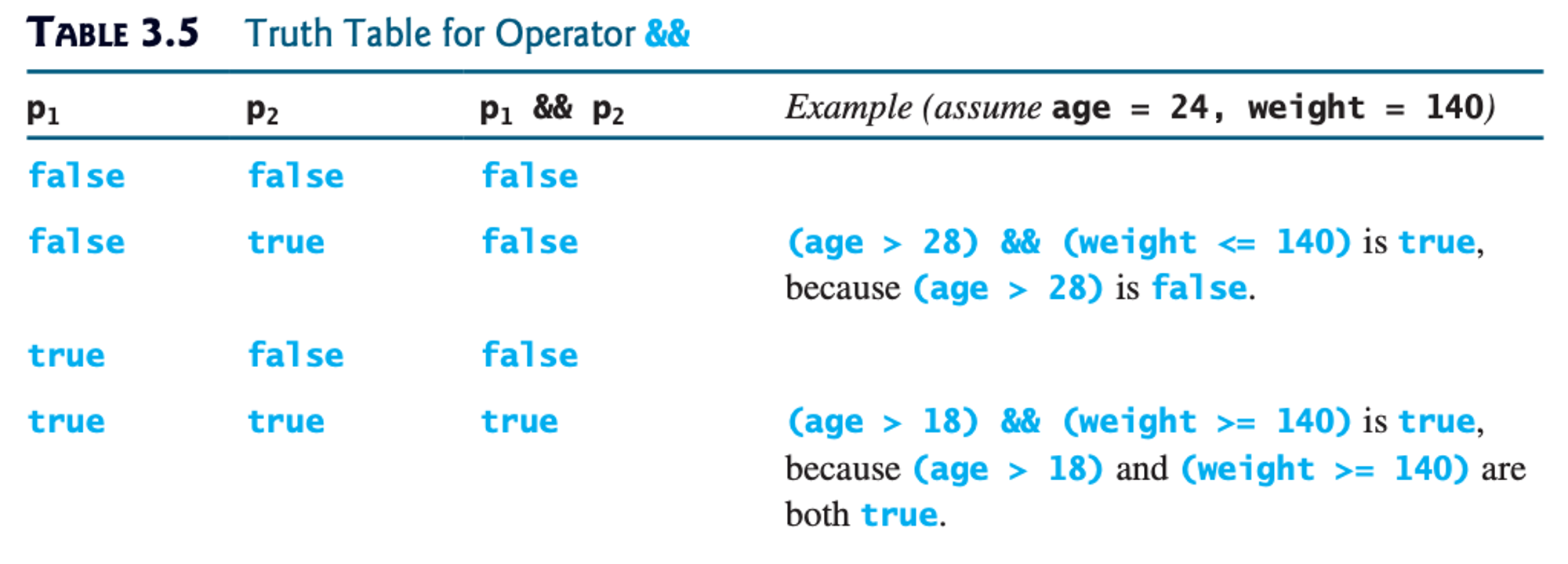
Credit: Y. Daniel Liang, Introduction to Java Programming (Comprehensive Version), 10th ed.
NOTE: There is an error in the first example. It should say that the overall expression is false because (age > 28) is false.
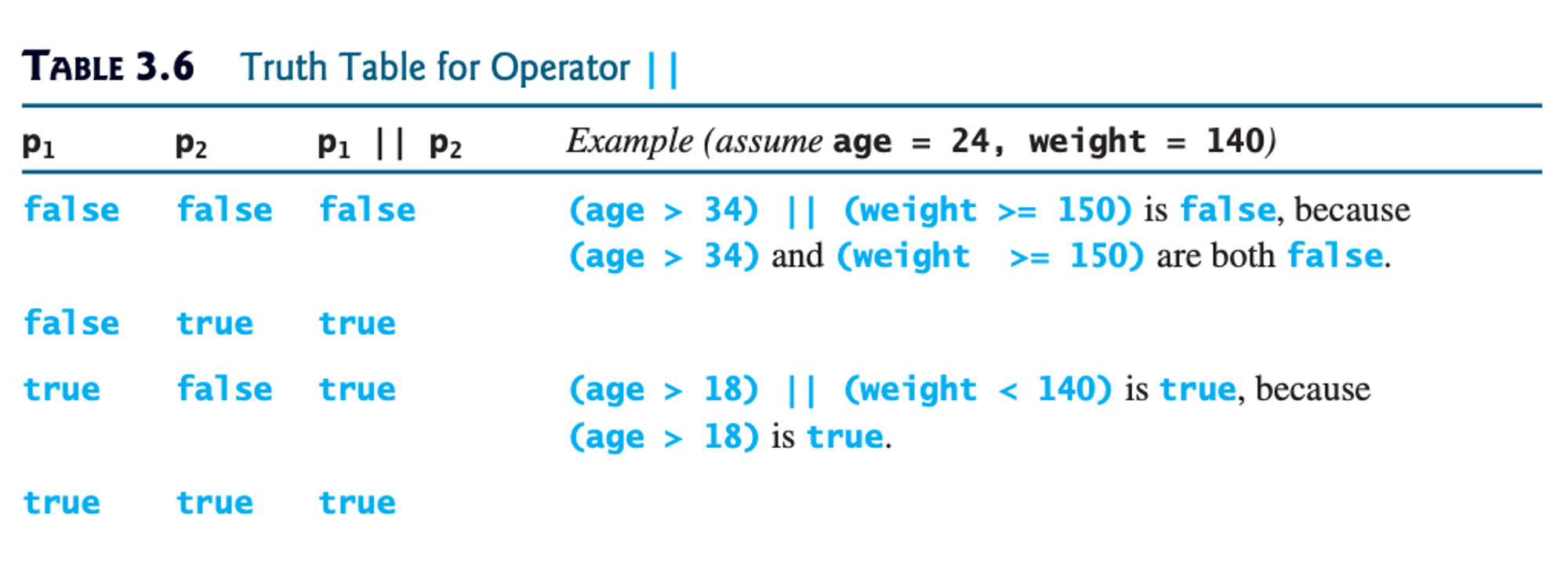
Credit: Y. Daniel Liang, Introduction to Java Programming (Comprehensive Version), 10th ed.
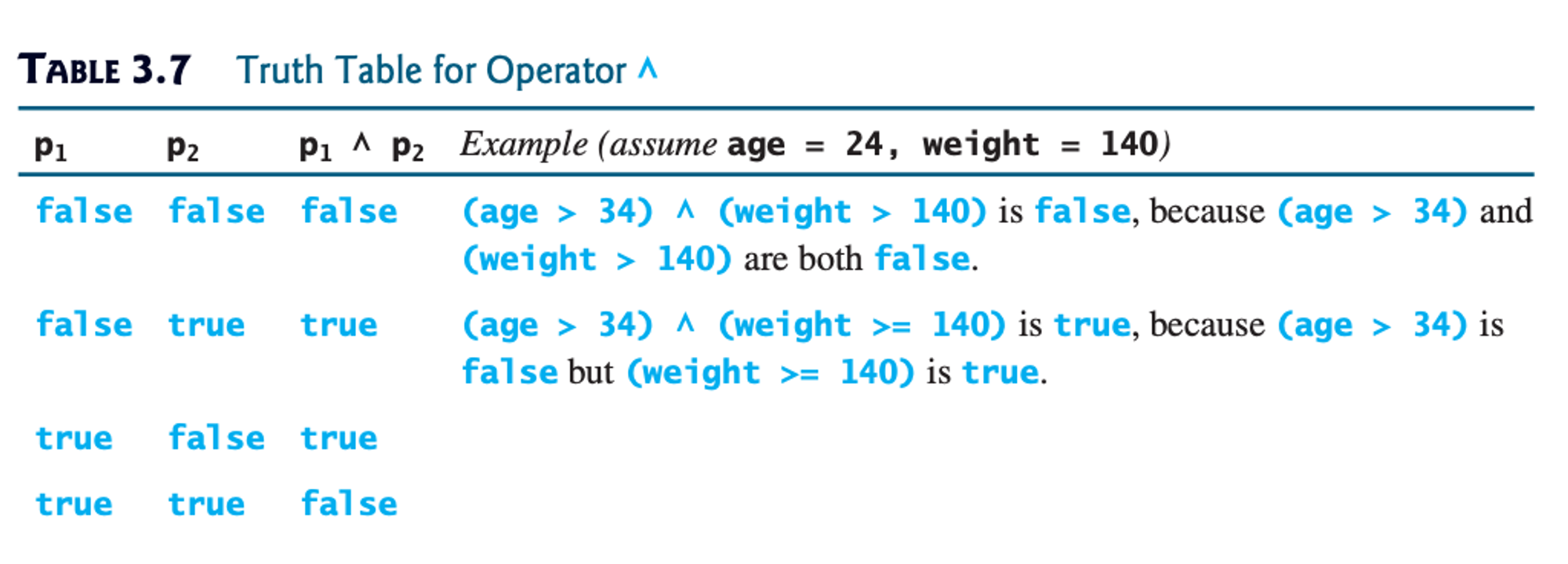
Credit: Y. Daniel Liang, Introduction to Java Programming (Comprehensive Version), 10th ed.
There is also a unary logical operator, the logical NOT.

Credit: Y. Daniel Liang, Introduction to Java Programming (Comprehensive Version), 10th ed.
Practice
Logic
Given the code in the practice template, predict what the output of this program will be. Write your answers as comments on the program next to the print statements.
Previous Section
6.2 Relational OperatorsNext Section
6.4 If and ElseCopyright © 2021 Code 4 Tomorrow. All rights reserved.
The code in this course is licensed under the MIT License.
If you would like to use content from any of our courses, you must obtain our explicit written permission and provide credit. Please contact classes@code4tomorrow.org for inquiries.